Description
Synonyms: 3,6-Anhydro-α-L-galacto-β-D-galactan, Agarose LE
General description
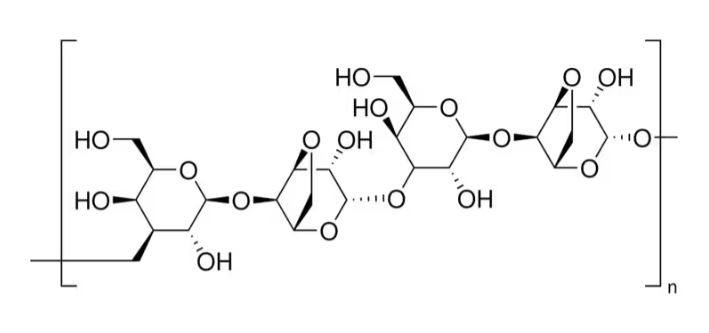
Agarose is a natural polysaccharide isolated from the seaweed genera Gelidium and Gracilaria. Structurally, it is a linear polymer consisting of alternating D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose units.
Application
Agarose has been used:
- in gel electrophoresis to analyze the integrity of DNA
- to prepare hydrocolloid gels and study the structural influence of gels on the release of carbohydrates
- in gel electrophoresis to analyze the integrity of RNA
- it is suitable for protein applications such as Ouchterlony and radial immunodiffusion (RID)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Agarose serves as a gelling agent and is extensively used in molecular biology research to separate and analyze nucleic acids by gel electrophoresis or blotting (Northern or Southern). During gelation, agarose polymers combine non-covalently resulting in a network of bundles whose pore sizes decide a gel′s molecular sieving properties. The type and the concentration of agarose influence the rate of migration of a DNA molecule through a gel. However, agarose also has attractive features that bring about a strong interest in its usage in biological applications. It is known to mimic the extracellular matrix which makes it an excellent biomaterial for tissue engineering applications. Due to its great water uptake capability agarose is suitable for cell-encapsulation. Agarose allows regulated permeation for oxygen and nutrients and is useful in cell growth, differentiation, and proliferation. Agarose is used in controlled/localized drug delivery and regenerative medicine, such as neurogenesis, angiogenesis, spermatogenesis, cartilage formation, bone regeneration, wound healing, and artificial pancreas.
Features and Benefits
- Biocompatible
- Agarose gels have larger pore sizes than polyacrylamide gels at low concentrations
- Unlike polyacrylamide, the consistency of the gels is more solid (but also less elastic)
- Possesses low ethidium bromide and SYBR Green background staining
Analysis Note
The following is a list of properties associated with our agaroses:
Sulfate content – used as an indicator of purity, since sulfate is the major ionic group present.
Gel strength – the force that must be applied to a gel to cause it to fracture.
Gel point – the temperature at which an aqueous agarose solution forms a gel as it cools. Agarose solutions exhibit hysteresis in the liquid-to-gel transition – that is, their gel point is not the same as their melting temperature.
Electroendosmosis (EEO) – a movement of liquid through the gel. Anionic groups in an agarose gel are affixed to the matrix and cannot move, but dissociable counter cations can migrate toward the cathode in the matrix, giving rise to EEO. Since electrophoretic movement of biopolymers is usually toward the anode, EEO can disrupt separations because of internal convection.
Sulfate content – used as an indicator of purity, since sulfate is the major ionic group present.
Gel strength – the force that must be applied to a gel to cause it to fracture.
Gel point – the temperature at which an aqueous agarose solution forms a gel as it cools. Agarose solutions exhibit hysteresis in the liquid-to-gel transition – that is, their gel point is not the same as their melting temperature.
Electroendosmosis (EEO) – a movement of liquid through the gel. Anionic groups in an agarose gel are affixed to the matrix and cannot move, but dissociable counter cations can migrate toward the cathode in the matrix, giving rise to EEO. Since electrophoretic movement of biopolymers is usually toward the anode, EEO can disrupt separations because of internal convection.
PROPERTIES
biological source
algae (marine)
Pack Size
100g; 250g; 500g
grade
for molecular biology
product line
BioReagent
form
powder
technique(s)
electrophoresis: suitable
impurities
≤10% moisture content
EEO
0.09-0.13
transition temp
gel point 36 °C ±1.5 °C (1.5% gel)
gel strength
≥1200 g/cm2 (1% gel)
anion traces
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.15%
suitability
suitable for electrophoresis
suitable for molecular biology
foreign activity
DNase, RNase, none detected


![Propan-2-ol uniLAB® [2.5 Litres]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/826-Propan-2-ol-200x200.jpg)
![Universal indicator solution uniLAB, Merck [100ml]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/276-pH-indicator-soln-300x300.jpg)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.