Description
Synonyms: Membrane Fecal Coliform Agar, m-Fecal Coliform Agar
Application
An agar suitable for the detection and enumeration of faecal coliforms by the membrane filtration technique.
Mode of Action
In the beginning the faecal coliforms, derived from the intestinal tract of warm-blooded animals, were separated from the nonfaecal coliforms by use of elevated temperature tests, which needed confirmatory MPN procedure in addition. GELDREICH et al. published the development of a Faecal Coliform (FC) Medium
for the membrance filtration technique using an incubation temperature of 44.5 °C ± 0.2 °C.
In the beginning the faecal coliforms, derived from the intestinal tract of warm-blooded animals, were separated from the nonfaecal coliforms by use of elevated temperature tests, which needed confirmatory MPN procedure in addition. GELDREICH et al. published the development of a Faecal Coliform (FC) Medium
for the membrance filtration technique using an incubation temperature of 44.5 °C ± 0.2 °C.
m-FC Agar is supplemented with rosolic acid and incubated at 44.5 °C ± 0.2 °C for 24 h.
Peptone and yeast extract serve as nutritious source and bile salts are added to inhibit accompanying Gram-positive flora.
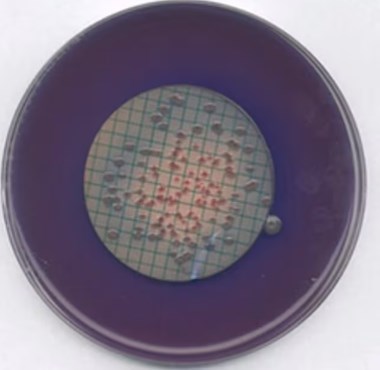
Lactose can be fermented by faecal coliforms at the elevated temperature to form blue colonies on the ready medium (agar base plus rosolic acid), whereas other organisms show grey colonies.
Peptone and yeast extract serve as nutritious source and bile salts are added to inhibit accompanying Gram-positive flora.
Lactose can be fermented by faecal coliforms at the elevated temperature to form blue colonies on the ready medium (agar base plus rosolic acid), whereas other organisms show grey colonies.
Typical Composition (g/litre)
Proteose peptone 5.0; tryptose 10.0; yeast extract 3.0; sodium chloride 5.0; bile salts 1.5; lactose 12.5; methyl blue (formerly aniline blue) 0.1; agar-agar 15.0.
Proteose peptone 5.0; tryptose 10.0; yeast extract 3.0; sodium chloride 5.0; bile salts 1.5; lactose 12.5; methyl blue (formerly aniline blue) 0.1; agar-agar 15.0.
Preparation
Suspend 52 g in 1 litre of distilled or deionized water and heat to boiling to dissolve completely. Add 10 ml of a 1 % solution of rosolic acid in 0.2 N NaOH. Continue heating for 1 minute with frequent agitation. Do not autoclave! Cool to 45-50 °C. Dispense 4 ml amounts into Petri dishes (Æ 50-60 mm) and allow to solidify. Cool to 50 °C and pour plates.
pH: 7.4 ± 0.2 at 25 °C.
The plates are clear and blue to violet.
Suspend 52 g in 1 litre of distilled or deionized water and heat to boiling to dissolve completely. Add 10 ml of a 1 % solution of rosolic acid in 0.2 N NaOH. Continue heating for 1 minute with frequent agitation. Do not autoclave! Cool to 45-50 °C. Dispense 4 ml amounts into Petri dishes (Æ 50-60 mm) and allow to solidify. Cool to 50 °C and pour plates.
pH: 7.4 ± 0.2 at 25 °C.
The plates are clear and blue to violet.
Experimental Procedure
Place membrane filter, through which the sample has been filtered, on the surface of the agar. Avoid formation of air bubbles between the filter and the agar surface.
Incubation: 24 hours at 44.5 °C ± 0.2 °C aerobically.
Place membrane filter, through which the sample has been filtered, on the surface of the agar. Avoid formation of air bubbles between the filter and the agar surface.
Incubation: 24 hours at 44.5 °C ± 0.2 °C aerobically.
Evaluation
Blue coloured colonies on the membrane filter are counted as faecal coliforms. Other organisms form grey to cream colonies.
Blue coloured colonies on the membrane filter are counted as faecal coliforms. Other organisms form grey to cream colonies.
PROPERTIES
composition
Agar, 13.0 g/L
Aniline Blue, 0.1 g/L
Bile Salts No 3, 1.5 g/L
Lactose, 12.5 g/L
Peptone, 5.0 g/L
Sodium chloride, 5.0 g/L
Tryptone, 10.0 g/L
Yeast Extract, 3.0 g/L
packaging
poly bottle of 500 g
pH
7.4±0.2 (25 °C)
storage temp.
15-25°C
![Magic Wipes Cleaning Cloths [Pack of 50]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/396-Magic-wipes-300x300.jpg)

![Oxidase Test Strips [Pack of 100]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/023-Bactident-oxidase-strips-300x300.jpg)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.