Description
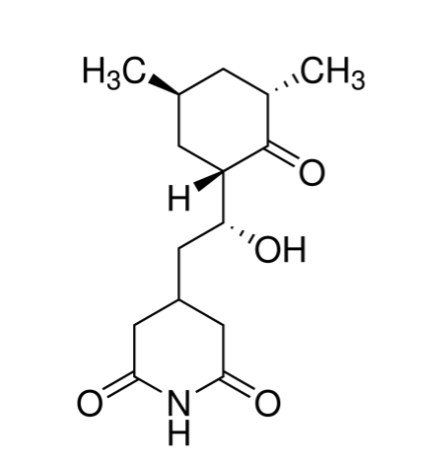
Synonyms: 3-[2-(3,5-Dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]glutarimide, Actidione, Naramycin A
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation): C15H23NO4
DESCRIPTION
Application
- In yeast strains, cycloheximide has been used as a protein synthesis inhibitor in the cycloheximide chase experiment.
- It has been used to inhibit translation in mammalian cells.
- It has been used to suppress fungal growth.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cycloheximide (CHX) is an antibiotic produced by S. griseus. Its main biological activity is translation inhibition in eukaryotes resulting in cell growth arrest and cell death. CHX is widely used for selection of CHX-resistant strains of yeast and fungi, controlled inhibition of protein synthesis for detection of short-lived proteins and super-induction of protein expression, and apoptosis induction or facilitation of apoptosis induction by death receptors.
PROPERTIES
biological source
microbial
Assay
≥94% (TLC)
form
powder
solubility
ethanol: soluble, clear to hazy
antibiotic activity spectrum
fungi
yeast
Mode of action
protein synthesis | interferes
storage temp.
2-8°C
![Propan-2-ol uniLAB® [2.5 Litres]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/826-Propan-2-ol-200x200.jpg)


![Universal indicator solution uniLAB, Merck [100ml]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/276-pH-indicator-soln-300x300.jpg)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.