Description
Synonyms: D(+)-Saccharose, α-D-Glc-(1→2)-β-D-Fru, α-D-Glucopyranosyl β-D-fructofuranoside, Sugar, β-D-Fructofuranosyl-α-D-glucopyranoside
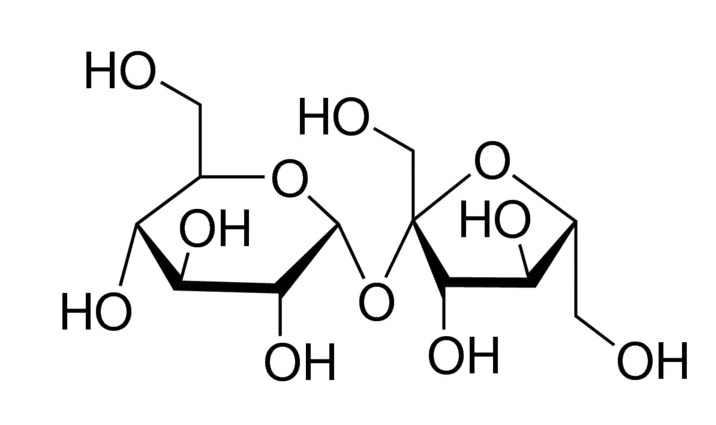
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation): C12H22O11
General description
Sucrose is used to prepare density gradients for cell/organelle separation. In addition, sucrose can be used as a supplement in plant, insect, and bacterial culture media. It can also be used in various enzymatic assays.
Application
Sucrose has been used:
- to perform cryoprotection for kidney tissues
- as a component in the solid germination medium to germinate pollen grains
- in the triphenyl-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) test to check the viability of pollen grains
- in the cryoprotection of fixed brain tissues for immunohistochemistry
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
- Ideal for Molecular Biology, Cell Biology and Biochemical research
- Tested to confirm low levels of heavy metal contamination, ensuring suitability for various applications
- Tested for DNase, RNase, and proteases
- Molecular biology grade sucrose, sourced from sugar cane
PROPERTIES
biological source
sugar cane
Pack Size
500g
grade
for molecular biology
Assay
≥99.5% (GC)
form
crystals
technique(s)
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
impurities
≤0.1% free glucose
color
white
useful pH range
5.5-7 (25 °C, 342 g/L)
mp
185-187 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: soluble 50 g + 50 mL
cation traces
heavy metals (as Pb): ≤5 ppm
absorption
≤0.15 at 280 at 50%
≤0.20 at 260 at 50%
application(s)
agriculture
foreign activity
DNase, RNase, protease, none detected
storage temp.
room temp
![Tryptic Soy Agar + LTHTh - ICR, 90mm settle plates [Pack of 20]](https://idealmedical.co.za/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/136-Tryptic-soy-ICR-300x300.jpg)


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.