Description
General description
Methanol undergoes thermochemical conversion to C2-C10 hydrocarbons in the presence of shape-selective zeolites has been reported. Its oxidation on Ru-Pt catalyst system by ruthenium ad-atoms has been proposed.
Methanol is an organic solvent that can be synthesized from syngas in the presence of CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts. It is an ideal candidate as a hydrogen source in fuel cell technology due to its high H/C ratio, low propensity for soot generation, relatively low reforming temperature and as it exists in liquid state at room temperature. In a direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC), methanol undergoes oxidation with air to generate electricity. The olefins (ethylene or propylene) formed from methanol via MTO (methanol-to-olefins) process, can be an alternative to oil and gas to produce hydrocarbon fuels.
Application
Methanol has been used as a solvent for the sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of alkaline protease isoforms isolated from larva of the spotted sand bass (Paralabrax maculatofasciatus). It has been used in the isolation and quantitative determination of carotenes and xanthophylls from Capsicum annum pericarp extracts by HPLC.
PROPERTIES
grade
ACS reagent
vapor density
1.11 (vs air)
vapor pressure
410 mmHg ( 50 °C)
97.68 mmHg ( 20 °C)
assay
≥99.8%
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
725 °F
expl. lim.
36 %
impurities
H2SO4, passes test (darkened)
MnO4- reducers, passes test
≤0.0002 meq/g Titr. base
≤0.0003 meq/g Titr. acid
≤0.001% acetaldehyde
≤0.001% acetone
≤0.001% formaldehyde
≤0.1% water
evapn. residue
≤0.001%
color
APHA: ≤10
clear
refractive index
n20/D 1.329 (lit.)
bp
64.7 °C (lit.)
mp
−98 °C (lit.)
density
0.791 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
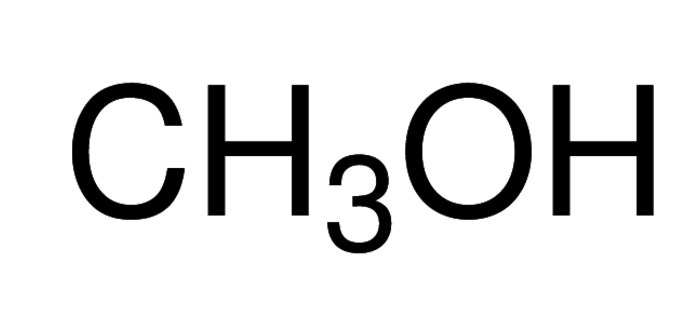

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.